Flavonoids are phytochemical compounds found in flowers, fruits, and vegetables, not just marijuana. They are responsible for the pigmentation, scent, and flavor of natural flora.

What are Flavonoids?

The term Flavonoid comes from the latin Flavus, meaning yellow, refering to the color of their pigmentation.
They are made up of polyphenolic compounds (more than one phenol group in their chemical structure) found in the plant kingdom. In general, their chemical structure is a Carbon skeleton made up of 15 water-soluble Carbon atoms with two benzene rings connected by a three-liked Carbon chain.
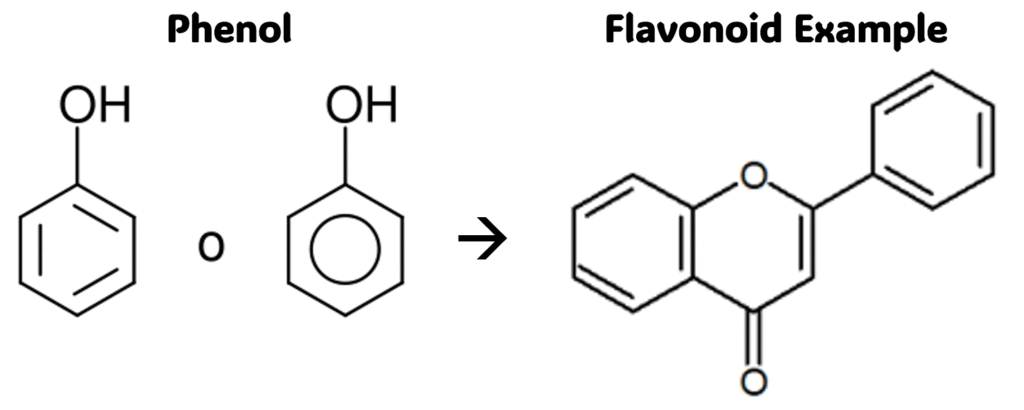
More than 10,000 Flavonoids have been identified and isolated.
Flavonoids are responsible for the vibrant colors and unique flavors of plants; and in cannabis in particular they are found primarily in the seedlings, leaves, and flowers, and not in the roots or seeds.
They interact with Cannabinoids and Terpenes, which is why they might enhance the therapeutic properties of cannabis.
Flavonoids possess antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antiviral, and antibacterial properties. They also contribute to the sensory perception of cannabis, influencing flavor and overall experience.
In addition, these polyphenols perfom functions such as protection from sunlight attracying pollinators and defending against predators.
What coloration do Flavonoids give to cannabis?
Flavonoids can produce a wide range of colors; from yellow to purple and red.
It’s worth mentioning that in cannabis, as in other plants, the yellow color of some flavonoids can be overshadowed by the green color of Chlorophyll (which is not a Flavonoid). The presence of these compounds is not evident to the naked eye, but is hidden beneath the various shades of green. Sometimes, however, the purple or red color of marijuana betrays their presence.
Flavonoids functions in plants
Flavonoids are found in many plants and can serve various purposes, but one of their main functions is their role as pigments, particularly in flower’s color.
More than 4,000 types of natural Flavonoids have been discovered. Some people also suggest that these compounds may play an important role protecting the plant from ultraviolet light and disease.
Flavonoids are essential compounds for plant survival and also give a distinctive character to many marijuana strains.
Flavonoid’s subcategories
There are 6 (Chalcones, Flavones, Isoflavonoids, Flavanones, Anthoxanthins and Anthocyanins):
1. Chalcones

These Flavonoids give rise to the brown hues found in nature.
Tomatoes and apples are excellent examples of fruits and vegetables with abundant concentrations of Chalcones.
2. Flavones

Flavones are one of the essential subcategories of flavonoids and are responsible for the yellow hues found in nature.
In this subcategory exist some called Canflavins, wich we mention briefly now.
What are Cannflavins?
Cannflavins are Flavonoids found exclusively in cannabis and belong to the Flavones subcategory.
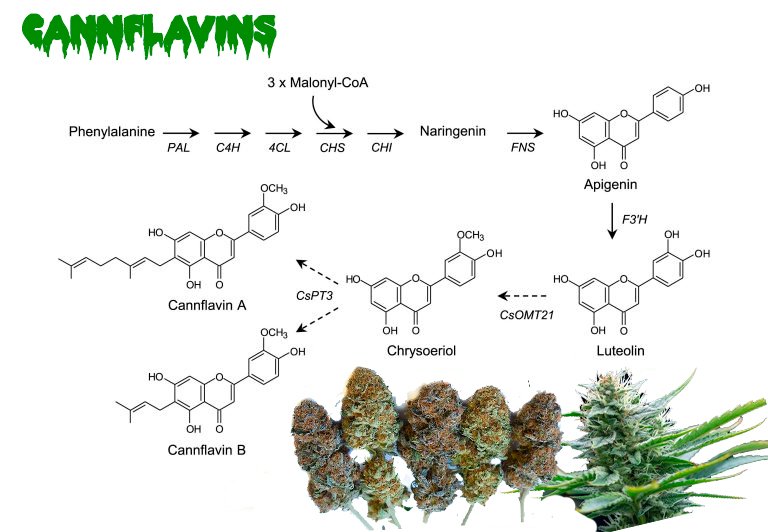
Cannflavins A, B and C are Flavonoids that have been shown to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that benefit health.
Flavones, are found in Celery, Chamomile, Parsley and Mint.
3. Isoflavonoids

These are very broad subgroup of Flavonoids and, as such, cover a very diverse spectrum of colors, from white to dark purple.
4. Flavanones

Flavonones produce orange hues.
In nature, high concentrations can be found in fruits of the citrus family.
5. Anthoxanthins
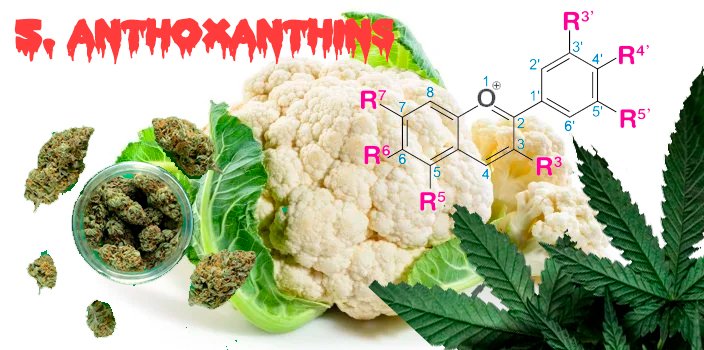
Anthoxanthins produce creamy white and yellow colors, visible in plant petals, cauliflower, mushrooms, or potatoes.
6. Anthocyanins
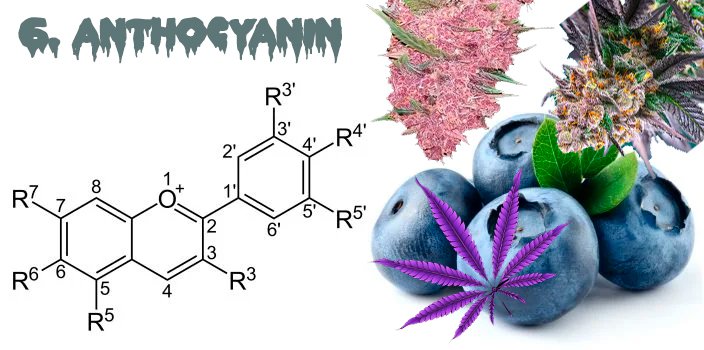
Anthocyanins are responsible for the dark hues observed during the flowering stage, ranging from deep purples to lighter purples like violet, vivid reds, and brilliant blues.
Blueberries, Plums, Eggplants and Cannabis are high in Anthocyanins.
Minor Flavonoids
They correspond to: β-sitosterol, Vitexin, Luteolin, Isovitexin, Apigenin, Kaempferol, Quercetin and Orientins.
1. β-sitosterol
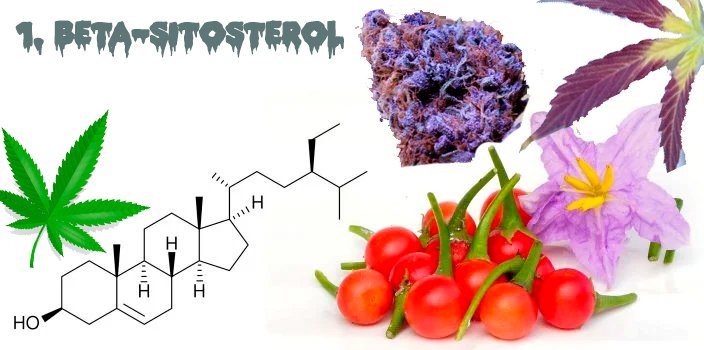
This minor Flavonoid is related to cholesterol and can be found in many fruits, vegetables, nuts, spices, and seeds.
2. Vitexin

Vitexin is present in bamboo leaves and in Passion Flower.
3. Luteolin

The yellow petals of Reseda luteola, famous for their high concentration of Luteolin, have been used for centuries to produce natural yellow dyes.
It can be found in carrots and peppers.
4. Isovitexin
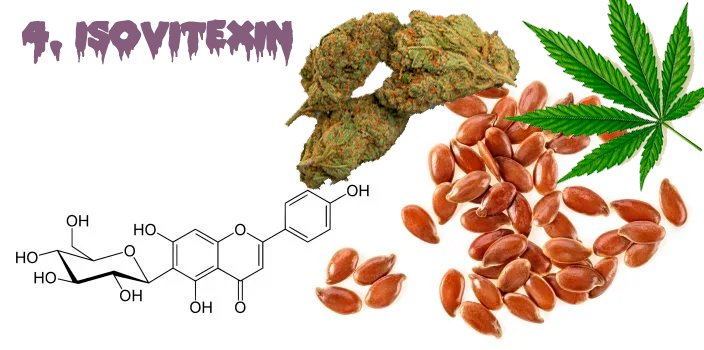
Isovitexin is an isotype of Vitexin, and is found naturally in buckwheat, cereals, flax, and cannabis.
5. Apigenin
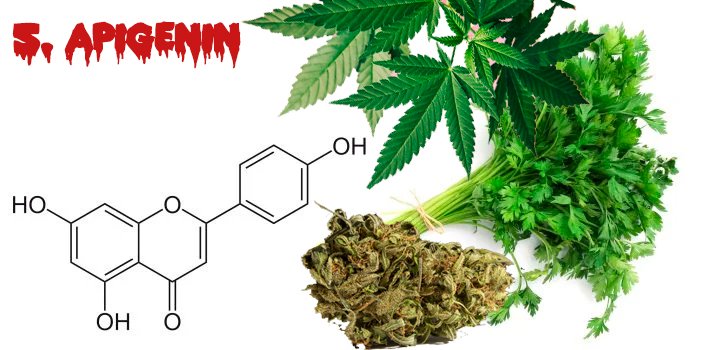
Apigenin is one of the most widespread Flavonoids in nature and is found in Onions, Parsley and Celery.
6. Kaempferol
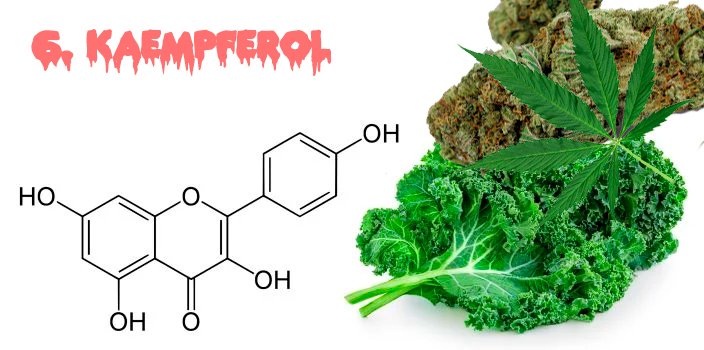
Kaempferol is present in many vegetables such as spinach.
7. Quercetin

Quercetin is present in high concentrations in pink onions, cereals, blueberries, and tomatoes.
It is among the ten most common flavonoids in cannabis.
8. Orientins
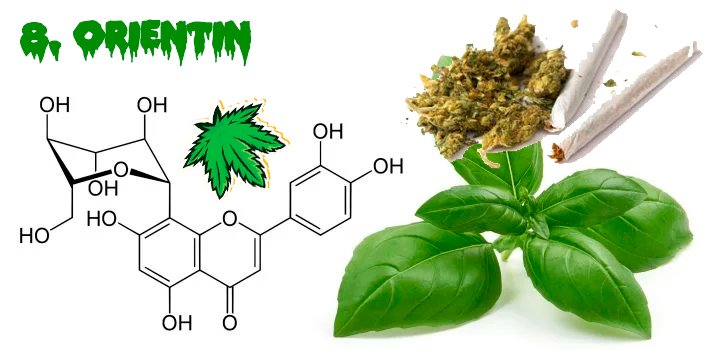
Orientin has been found in basil leaves.
Marijuana Flavonoids and the endocannabinoid system

The endocannabinoid system is a diverse cellular signaling network comprising endocannabinoids, CB1 and CB2 receptors, and corresponding enzymes. Its primary function is to help balance and regulate essential bodily functions by maintaining homeostasis (the internal equilibrium necessary for vital functions).
Endocannabinoid receptors are found throughout the body, with the highest concentration located in the central nervous system (CNS), including the neocortex, cerebellum, and spinal cord. CB2 receptors, on the other hand, are found primarily in the peripheral immune system (PIS).
Flavonoids act synergistically with these cannabinoid receptors and cannabis compounds to enhance the effects of minor phytocannabinoids.
The endocannabinoid system plays a crucial role in how we react to marijuana use and can help mediate the effects of phytocannabinoids. It can also regulate and control a multitude of functions, such as sleep and appetite.